Disease-information
The Lancet: Published on October, 2022Hypertension, or high blood
pressure, is a key risk factor for cardiovascular disease worldwide. Previous clinical trials supporting
the cardiovascular benefits of antihypertensive therapy primarily use
conventional morning dosing. Additionally, cardiovascular events
are temporally associated with the morni...
Neurology (American Academy of Neurology) Journal: Published on March,
2022Severe acute respiratory
syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can cause long-term disability (long COVID)
with new neurologic manifestations after even mild infections. Reports of peripheral
neuropathy include Guillain-Barré syndrome, mononeuritis multiplex, brachial
ple...
European Heart Journal: September, 2022Cardiovascular (CV) disease (CVD) is the leading cause of
morbidity and mortality worldwide, despite continuous improvement of medical
treatment, diagnosis, and risk factor control. It has been clearly
demonstrated that statin therapy confers significant mortality and morbidity
benefits in both the primary...
The Lancet: Published on September, 2022A
promising malaria vaccine was up to 80% effective at preventing the disease in
young children who received a booster shot at one year following a primary
three-dose regime maintained high efficacy against malaria, and continued to
meet the World Health Organization’s Malaria Vaccine Technology Roadmap g...
Journal of the American
Heart Association (AHA): Published on November, 2022Sleep, alongside diet and physical activity (PA), is one of
the 3 pillars of health, but unlike other health behaviors, healthy sleep is
not included in the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association
(AHA) cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention guideline...
Nature Medicine: Published on November, 2022Obesity is a chronic, relapsing
disease with a substantial morbidity, mortality, and healthcare burden. Drug
interventions for the treatment of obesity provide a potential valuable adjunct
to lifestyle interventions, which often achieve only limited weight loss that
is difficult to maintain. Semagluti...
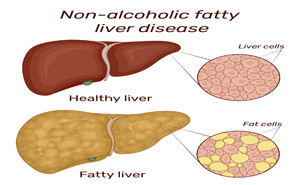
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM): Published
On October, 2022Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD) is associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D), causing
substantial burden from hepatic and extrahepatic complications.TAKE-HOME MESSAGEThis review discusses practical
approaches to the management of patients wit...
Journal of the American College of Cardiology: Published on December,
2022Healthy dietary patterns are rich
in micronutrients, but their influence on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risks
has not been systematically quantified.The goal of this study was to
provide a comprehensive and most up-to-date evidence-based map that
systematically quantifi...
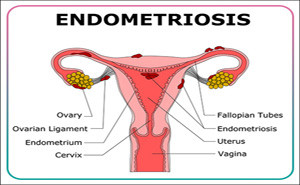
MIDDLE EAST JOURNAL OF FAMILY MEDICINE: Published on November, 2022A Systematic Review and
Meta-AnalysisEndometriosis is a chronic, estrogen-dependent disease that
affects 10-15% of women in their reproductive age. It is characterized by the
presence of endometriallike tissues outside the uterine cavity that induce
chronic inflammation, ovarian...
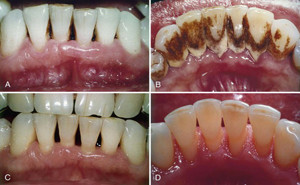
Journal of Clinical
Medicine: Published
on November 2022Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of multifactorial
origin, characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. The main etiological factors for the disease include
gram-negative anaerobic bacteria and a variety of facultative bacteria that
reside in the subgingival biofilm.Var...
JAMA Pediatrics: Published on November 2022A Systematic Review and Meta-analysisTAKE-HOME MESSAGEAre shorter courses of
antibiotics as good as longer courses?This systematic review and meta-analysis assessed whether
shorter courses of antibiotics are noninferior to longer courses of antibiotics
for nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in...
JAMA Pediatrics: Published on November 2022A Systematic Review and Meta-analysisTAKE-HOME MESSAGEAre shorter courses of
antibiotics as good as longer courses?This systematic review and meta-analysis assessed whether
shorter courses of antibiotics are noninferior to longer courses of antibiotics
for nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) in...