Drugs-for-dyspepsia
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics:
Functional dyspepsia is
characterised by troublesome early satiety, fullness, or epigastric pain or
burning. It can easily be overlooked as the symptoms overlap with
gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and irritable bowel syndrome.
It affects 10% of the population
and is more prevalent in women....
TAKE-HOME MESSAGEAbout 80%
of pregnant women suffer from gestational reflux disease. Most
interventions are based on a “step-up” approach that begins with lifestyle
modifications. If the
symptoms persist despite lifestyle modification, a medical intervention can be
considered.
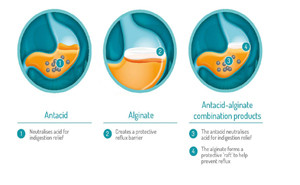
Antacids,
alginates and sucralfate are the first-line t...
Antacids neutralize gastric acid
and are, broadly used in the
treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in adults. They are
utilized for more than 2,000 years, though evidence of the effectiveness and
safety is limited in infants [1]. Antacids have an effect on the short-term
relief of heartburn and the healing of esophagitis. Charac...
Dyspepsia is defined as having one
or more symptoms of epigastric pain, burning, postprandial fullness, or early
satiation. Bloating and nausea often coexist
with dyspepsia but are nonspecific and are thus not included in its definition.
Heartburn is also excluded from diagnostic symptom criteria for dyspepsia since
it is thought to primarily...
Comparative study of PPI for symptom
relief in patients with reflux esophagitis:
Some of the present study demonstrated
that esomeprazole gave faster symptom relief than pantoprazole, lansoprazole
and omeprazole.
Because:
Esomeprazole has been shown to have a
faster onset of anti-secretory...