Disease-information
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) & The New England Journal of
Medicine (NEJM):
Key Prescribing Notes:
Perioperative bleeding is common
complications in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery, is associated with
increased morbidity and mortality.
The goal of the POISE-3 trial was
to determine whether tranexamic acid, when u...
Journal of Endometriosis and Pelvic Pain Disorders:
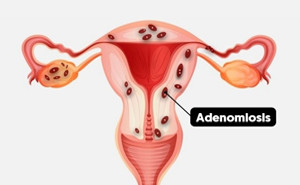
Adenomyosis is a common
gynecological disease in premenopausal women and late reproductive age. The
most common symptoms are progressive dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain,
dyspareunia, heavy menstrual bleeding, and abnormal uterine bleeding.
The severity and frequency of symptoms...
Overview of OsteoporosisOsteoporosis is a disease
characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue and bone
structure, which can lead to increased bone fragility and risk of fracture. The most common fractures associated
with osteoporosis are in the hip, spine, wrist, and shoulder.
Osteoporosis is the major cause
o...
Nature Medicine
Post-acute
sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)—can
involve the pulmonary and several extrapulmonary organs, including the
cardiovascular system. A few studies have investigated cardiovascular outcomes
in the post-acute phase of the COVID-19; however, most were limited to
hospitalized...
Children who are infected with
COVID-19 are at a higher risk of developing diabetes, according to a new study
by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Increased incidence of
diabetes seen among patients aged younger than 18 years after acute COVID-19
infection versus those without COVID-19.
Key Summary
What is already...
The Lancet:
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
It is well-established that blood pressure control is an
important strategy in reducing cardiovascular events among people with
diabetes.
This data analysis that included studies comprised of over
145,000 participants finds that a reduction of 5 mm Hg in systolic blood
pressure was associated with an...
The Lancet:
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
It is well-established that blood pressure control is an
important strategy in reducing cardiovascular events among people with
diabetes.
This data analysis that included studies comprised of over
145,000 participants finds that a reduction of 5 mm Hg in systolic blood
pressure was associated with an...
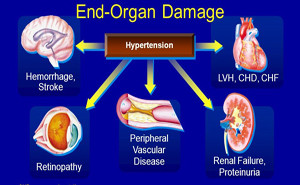
In accordance with most major
guidelines it is recommended that hypertension be diagnosed when a person’s
systolic blood pressure (SBP) in the office or clinic is ≥140 mm Hg and/or
their diastolic blood pressure (DBP) is ≥90 mm Hg following repeated
examination.Hypertension is the leading risk
factor for morbidity and mortality throughout the...
High
blood pressure is the leading cause of mortality and cardiovascular disease
globally, and most of the disease burden occurs in low- and middle-income
countries. Recent guidelines recommend lower blood pressure targets
among high-risk patients, increasing the need for more effective treatment
strategies.Treatment with a pill combining low...
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
The
authors investigated physician adherence with recommending peptic ulcer
disease (PUD) prophylaxis for elderly patients who were receiving dual
antiplatelet therapy or anticoagulation or who were at risk of bleeding
PUD, as per expert consensus guidelines from the American College of
Gastroenterol...
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a
chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the esophagus. Symptoms of EoE includes
vomiting, dysphagia, or feeding difficulties. Genetic factors and environmental
factors, such as exposure to antibiotics early in life, are associated with
EoE.TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
EoE affects approximately 34.4/100,000 peo...
Peptic ulcer disease is often defined as a mucosal break
greater than 3-5 mm in the stomach or duodenum with a visible depth. It is
therefore an endoscopic diagnosis in contrast to dyspepsia, which is a clinical
diagnosis based on symptoms alone. Peptic ulcer disease results from an
imbalance between factors that protect the mucosa of the stoma...