Disease-information
Key Information:
Respiratory
syncytial virus (RSV) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally in
preschool children with acute lower respiratory infections.
Current
guidelines do not support the routine use of antibiotics in these children. However, higher incidence of bacterial co-infection with RSV
bronchopulmonary infe...
Key Information:
Respiratory
syncytial virus (RSV) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally in
preschool children with acute lower respiratory infections.
Current
guidelines do not support the routine use of antibiotics in these children. However, higher incidence of bacterial co-infection with RSV
bronchopulmonary infe...
JAMA Network: A Systematic Review
and Meta-analysis
Osteoporosis is characterized by
reduced bone mass and fragmentation of bone architecture, resulting in an
increased risk of fracture. Approximately 1 in 2 women and 1 in 5 men aged 50
years or older will experience an osteoporotic fracture in their remaining lifetime.
Hip fracture is...
JAMA Surgery:
Surgical
site infections (SSIs) are infections of the incision or organ or space that
occur after surgery. Surgical patients initially seen with more
complex comorbidities and the emergence of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens
increase the cost and challenge of treating SSIs. The prevention of SSI is
increasingly important...
Osteoporosis is a bone disorder
that increases a person’s risk of fracture due to low bone mineral density
(BMD), impaired bone microarchitecture/mineralization, and/or decreased bone
strength. Osteoporotic fractures most commonly occur at the hip, spine and
wrist.
Fracture prevalence increases
dramatically with age. The majority of pos...
European Heart Journal:
Emerging as a new epidemic, long COVID or post-acute sequelae
of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a condition characterized by the
persistence of COVID-19 symptoms beyond 3 months. The long-term impact of COVID-19 on cardiovascular (CV) health and
mortality is also emerging as a major global concern.
Definit...
BioMed Central (BMC) Gastroenterology Journal:
Gastroesophageal
reflux disease (GERD) is one the most common medical complaints in
pregnant women. Its prevalence has been reported to reach as high as 80% in
certain populations. The prevalence of GERD is also increased as pregnancy
progresses from the first to third trimester. Some women...
European Heart Journal:
Worldwide, survivors of COVID-19
now exceed hundreds of millions, with some reporting incomplete recovery months
beyond the acute illness, a condition commonly referred to as long COVID.
Persistent symptoms of breathlessness, chest pain, fatigue, headaches, brain
fog, and palpitations are a constant reminder of th...
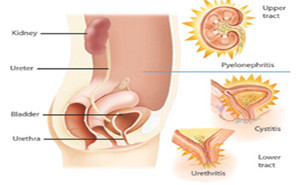
Asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB) is
seen in some healthy female populations and many women or men
with genitourinary tract abnormalities.
Although in many clinical
situations ASB is harmless, many patients with ASB are treated unnecessary.
Especially, long-term antimicrobial therapy of ASB may select for superinfection
with more antimicr...
Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) was commonly used worldwide, to
treat peptic ulcer disease (PUD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Helicobacter
pylori infection, or prevent side effects of glucocorticoids or
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). However, PPI agents were also
overused by off label indication, excessive dosage an...
International Journal of Dentistry:
Odontogenic infections are one of
the most prevalent diseases worldwide and the principal reason for seeking
dental care. Dental prescriptions account for nearly 7% to 11% of all common
antibiotic prescriptions.
The commonest emergency odontogenic
infections are periapical abscess (25%), pericoron...
The American Journal of Gastroenterology:
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a
class of effective medications used to treat various acid-related disorders.
Their use in the clinical setting has increased rapidly and tremendously. PPIs
are among the most commonly used medications worldwide.
However, the widespread
availability of these...