Dermatologic-disorders
International
Journal of Dermatology: June, 2024After
effective treatment, pruritus usually resolves gradually within 7–10 days, but
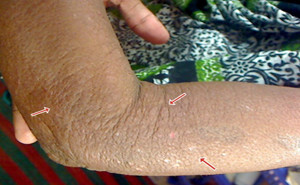
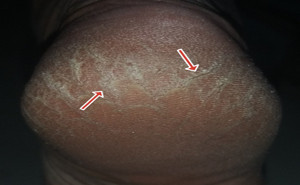
complete resolution may take up to 4 weeks.Scabies
mites can be found anywhere on the skin. Therefore, medication should be
applied to all areas of the body, itchy or not, except for the head:Special
care s...
International Journal of Dermatology: June, 2024Recent guidelines emphasize a
multimodal approach to scabies management, combining topical and systemic
therapies. First-line therapy: Topical Permethrin is recommended as first-line
therapy, with Benzyl benzoate, Sulfur ointment and Crotamiton as alternatives. Ivermectin remains a primary choice...
Xeroderma, also known as Dry skin, xerosis cutis, or
asteatosis, is a prevalent condition resulting from inadequate hydrolipids in
the skin.It manifests as roughness, tightness, scaling, and flaking,
often leading to pruritus, excoriations, and an increased risk of infections.
Factors contributing to xeroderma include environmental
c...
Cracked heels, or heel fissures, are caused by dry, thickened
skin around the heels, often resulting in discomfort, pain, and potential
complications like infections or cellulitis.Common in elderly individuals, diabetics, and those with
prolonged weight-bearing activities, contributing factors include dry skin,
improper footwear, medical condit...
The British Journal of Dermatology: Published: 16
September 2024Retinoids, widely used in
dermatology for treating acne and various skin conditions, have raised concerns
regarding potential side effects, particularly sexual dysfunction. Although
retinoids are effective in managing skin conditions, their association with sexual
dysfunction is b...
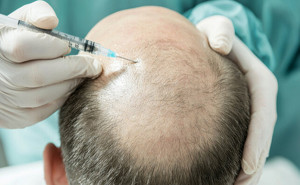
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology: July 2024Male androgenetic alopecia (AGA), or male pattern hair loss,
is characterized by gradual thinning of hair on the vertex of the scalp and
recession of the frontal hairline. FDA-approved therapies are restricted to topical minoxidil
and oral finasteride. Effective non–FDA-approved...
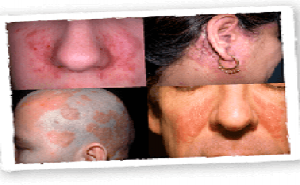
Archives of Dermatological Research: Published: August 2024Vitiligo, an autoimmune condition characterized by
depigmented skin patches due to the loss of functional melanocytes, has been
linked to dysregulation in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, particularly in
IFN-g signaling. The use of JAK inhibitors, such as ruxolitinib cream, a JAK1
and JA...
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology: Published
on December 2022Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is a
common chronic inflammatory skin disorder that most commonly affects young
adults, and less often children. In adolescents and adults, SD clinical
presentation may range from a mild scalp scaling to diffuse white, yellowish
patches in...
Importance:
Pityriasis versicolor generally clears
satisfactorily with treatment but often recurs when conditions are suitable for
malassezia to proliferate. It recurs when the weather becomes warm and humid
again. Regular use of topical treatment minimizes this risk. The color may
persist for weeks or months, particularly the hypopi...
Ketoconazole
is in a class of antifungal medications called imidazoles. It works by inhibiting
the growth of fungi that cause the infection.
Topical
ketoconazole is indicated for the treatment of cutaneous candidosis (including
vulvitis), tinea (pityriasis) versicolor and seborrhoeic dermatitis caused by
Malassezia (previously called Pi...
Journal of
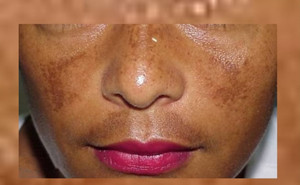
the American Academy of Dermatology: Published: September, 2023Melasma is a chronic pigmentary
disorder with a complex and multifactorial etiology. In this manuscript, the
authors present a set of consensus-based recommendations and provide a
comprehensive overview of how to manage melasma in daily clinical
practice. TAKE-HOME
MESS...
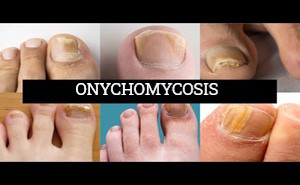
PubMed Central: Published June, 2019Onychomycosis is a fungal infection
occurring in the nails and may affect the adjacent skin. Typically, it
manifests as discoloration of the nail, nail plate thickening, and onycholysis.
It is the most common nail pathology and accounts for about 90% of toenail
infections worldwide.At present, there are sever...