Disease-information
The
management of Acute Gastroenteritis (AGE) is essentially based on 5 steps:
1. Assessment
of dehydration by simple, reproducible, and validated parameters and/or
clinical score;
2. Prompt
rehydration with reduced osmolality ORS;
3. Avoidance of
elimination diets and continuing of breast-feeding in infants and reg...
British Medical Journals (BMJ):
IntroductionProton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are
commonly prescribed drugs indicated for several gastric conditions, including
peptic ulcer disease, GERD and Barrett’s oesophagus.
Recent evidence suggests that PPIs
are commonly overprescribed, either in patients without an evidence-based
indication fo...
JAMA Internal Medicine:
Key Points
Question What
is the risk of perinatal complications associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection
during pregnancy and what factors are associated with hospitalizations?
Findings In
this cohort study of 43 886 pregnant individuals, SARS-CoV-2 infection during
pregnancy was associated with an increased ris...
Diabetes Journal: ADA publications
Several
randomized clinical trials have shown the possibility of preventing or delaying
the onset of type 2 diabetes in nondiabetic adults at high risk of developing
the disease. Successful interventions have included drugs (not further
discussed here) and lifestyle interventions emphasizing weight loss...
TAKE HOME MESSAGE
Acute pharyngitis is one of the most common complaints that a physician
encounters in the ambulatory care setting, accounting for 1% to 2% of all
ambulatory care visits annually and a high antibiotic prescribing rate.
However, the majority of these cases is viral and is self-limiting even in
cases caused by bacteria...
TAKE HOME MESSAGE
Acute pharyngitis is one of the most common complaints that a physician
encounters in the ambulatory care setting, accounting for 1% to 2% of all
ambulatory care visits annually and a high antibiotic prescribing rate.
However, the majority of these cases is viral and is self-limiting even in
cases caused by bacteria...
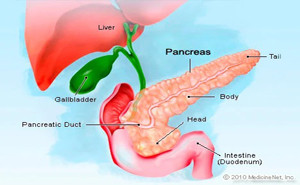
The American Journal of Gastroenterology
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
This nested case-control study
examined adults with gastric, liver, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers and use
of PPI for ≥2 years. Cancer risks for PPI dose and duration were also
evaluated.
While exploratory analysis found
an increased cancer risk for PPI use ≥10 years,...
The Pediatric Infectious
Disease Journal:
Clostridium difficile is an important cause of
antibiotic-associated diarrhea and the most widely recognized diarrheal
pathogen acquired in healthcare settings.
Antibiotic or gastric acid suppressant exposure, gastrointestinal feeding
devices, and certain medical conditions, such as malign...
The Pediatric Infectious
Disease Journal:
Clostridium difficile is an important cause of
antibiotic-associated diarrhea and the most widely recognized diarrheal
pathogen acquired in healthcare settings.
Antibiotic or gastric acid suppressant exposure, gastrointestinal feeding
devices, and certain medical conditions, such as malign...
Proton
pump inhibitors (PPIs) have been widely used for decades to treat acid-related
diseases. PPIs exhibit a well-established safety profile and reduce gastric
acid more effectively than histamine-2 receptor antagonists or antacids.
However,
observational studies suggest that long-term PPI therapy is associated with
osteoporotic fract...
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery:
Odontogenic infections are a common
problem in dentistry, and their treatment often requires the use of antibiotics
besides the removal of the source of infection, which frequently makes it more
difficult for clinicians to make a decision regarding the choice of antibiotic.
The pathogenesis...
Key Information
In the last decade, gastro-esophageal
reflux disease (GERD) and its complications of Barrett's oesophagus and
oesophageal adenocarcinoma are increasingly prevalent, especially in Asia. The
rise in GERD among Asians is largely attributed to a recent increase in the
prevalence of obesity.
Physiological dysfunction of the...