Drug-information
Ketoconazole
is in a class of antifungal medications called imidazoles. It works by inhibiting
the growth of fungi that cause the infection.
Topical
ketoconazole is indicated for the treatment of cutaneous candidosis (including
vulvitis), tinea (pityriasis) versicolor and seborrhoeic dermatitis caused by
Malassezia (previously called Pi...
Ophthalmology: The American Academy of Ophthalmology: Published:
January, 2024Sight loss from glaucoma is often
preventable with early diagnosis and treatment. Reducing IOP is the only proven
effective treatment for glaucoma. Better IOP control at an early stage reduces
the risk of further progression. Primary treatment options for
advanced gl...
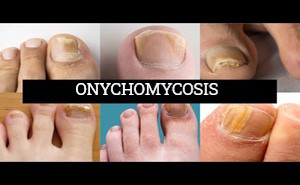
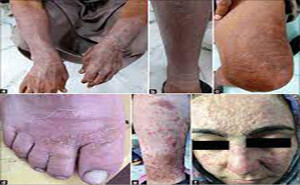
PubMed Central: Published June, 2019Onychomycosis is a fungal infection
occurring in the nails and may affect the adjacent skin. Typically, it
manifests as discoloration of the nail, nail plate thickening, and onycholysis.
It is the most common nail pathology and accounts for about 90% of toenail
infections worldwide.At present, there are sever...
Due to the changing face of
dermatophytosis in India, many dermatologists practice different dosing
patterns of itraconazole (ITZ). Recently, a new form of ITZ, super-bioavailable
ITZ (SBITZ), has been commercialized to overcome the pharmacokinetic challenges
of conventional ITZ (CITZ). ITZ is a weak base lipophilic
molecule with a limite...
International Journal of Research in Dermatology: March,
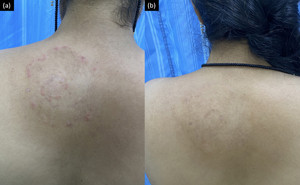
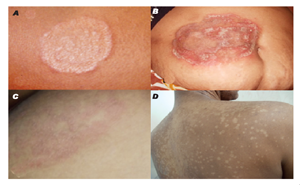
2022Tinea caused by trichophyton, microsporum, and epidermophyton is the most common fungal infection affecting 20–25% population globally, with varying geographic distribution.Due to Bangladesh’s hot and humid cli...
JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association: October,
2023Cefepime and
piperacillin-tazobactam are commonly administered to hospitalized adults for
empirical treatment of infection. Although piperacillin-tazobactam has been
hypothesized to cause acute kidney injury and cefepime has been hypothesized to
cause neurological dysfunction,...
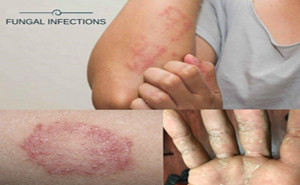
The prevalence of superficial
fungal infections across the globe is increasing from 20-25%. Superficial
infections are mostly caused by dermatophytes. Depending on the site affected,
the dermatophytes are clinically classified as Tinea capitis (head), Tinea
faciei (face), Tinea barbae (beard), Tinea manus (hand), Tinea corporis (body),
Tinea c...
Effect of Initial Treatment with Quadpill vs Standard Dose Monotherapy in Patients with Hypertension
Circulation: AHA
Journals: Published
July, 2023Hypertension management remains suboptimal globally, with
treatment inertia being identified as one of the main barriers to achieving
blood pressure (BP) control. Simpler approaches to achieve target BP levels are
needed. TAKE-HOME MESSAGEThe QUARTET study examined the
effectiveness of a quadrupl...
JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical AssociationThe authors investigated different
oral antifungal medications used to treat toenail fungal infections.TAKE-HOME MESSAGECompared
with placebo, high-quality evidence supports better clinical (ie, normal
appearance of the toenail) and mycological (negative culture, microscopy, or
both) results...
There has been a significant
increase in the incidence of chronic, relapsing, recurrent cases of superficial
dermatophytosis in India that are also often unresponsive to conventional drugs
and doses of recommended antifungal treatment. Almost 15– 20% of the outpatient
department cases are those of chronic dermatophytosis. Recurrences and relaps...
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications: August 2023Nearly one out of three individuals will develop a
psychiatric disorder during their life. Severe psychiatric disorders are
associated with higher mortality rates, with 10–20 life-years lost compared to
individuals without a severe psychiatric disorderSeveral psychiatric disorders are li...
Mycoses Journal: Published on April 2021Dermatomycoses of zoophilic origin,
especially those caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes, often pose considerable
therapeutic problems. This is reflected in the growing number of strains of
this species with resistance to terbinafine caused by a mutation in the
squalene epoxidase (SQLE) gene. TAKE HOME...