Gastrointestinal-hepatic-disorders
Pain is
defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) as ‘an
unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that
associated with, actual or potential tissue damage’.Most pain
is short-lived, resolving when the painful stimulus is removed or when tissue
healing has occurred: this is called acu...
Biliary colic is a common
presentation of a stone in the cystic duct or common bile duct of the biliary
tree. Colic refers to the type of pain that "comes and goes,"
typically after eating a large, fatty meal which causes contraction of the
gallbladder. However, the pain is usually constant and not colicky.History and Physical Examinations...
AACE Endocrine Practice Journal: Published
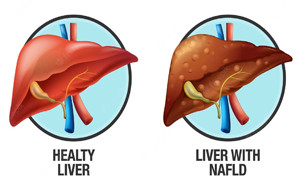
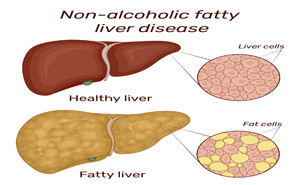
on May, 2022Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease affecting 25% of the
global population. NAFLD is associated with
cardiometabolic disorders: (1) obesity, (2) insulin resistance, (3) type 2
diabetes mellitus, (4) high blood pressure, and (5) at...
The American Academy of Physical
Medicine and Rehabilitation (AAPM&R): Physical medicine and
Rehabilitation (PM&R) Knowledge Journal:True visceral pain is a
physiologically and clinically separate entity from somatic pain.
Visceral pain responses are provoked by ischemia, inflammation, and distention.
Visceral pain is poorly defined and diffu...
The Lancet: Published on November, 2022Aspirin is widely recommended for the secondary prevention of
thrombotic vascular disease. Its use is
limited principally by increased risk of bleeding, particularly from the
gastrointestinal tract.The risks of upper gastrointestinal bleeding can be mitigated
in part by acid suppression with proton pump i...
BMJ Journals: Gut: Published on March, 2023Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is
a chronic immune-mediated disease of the bowel, comprising two main subtypes:
Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC).There is an increasing incidence of
inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) for which environmental factors is suspected.
Antibiotics have been ass...
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic,
progressive, fibroinflammatory lung disease associated with increased morbidity
and mortality. As its name suggests, the exact cause of the disease is not
known. However, some genetic and environmental factors have been
observed concurrently with the condition and are considered potential etiolo...
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM): Published
On October, 2022Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD) is associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D), causing
substantial burden from hepatic and extrahepatic complications.TAKE-HOME MESSAGEThis review discusses practical
approaches to the management of patients wit...
The American Journal of
Gastroenterology
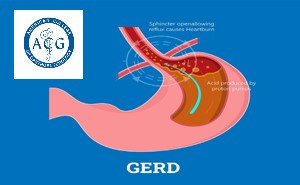
GERD MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Management
of GERD requires a multifaceted approach, taking into account the symptom
presentation, endoscopic findings, and likely physiological abnormalities.
Medical
management includes lifestyle modifications and pharmacologic therapy,
principally with medication...
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an
immune/antigen-mediated, progressive fibrostenotic disease characterized by
symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and abnormal eosinophilic infiltration in
the esophagus. Despite treatment modalities of
dietary antigen elimination or Topical corticosteroids, a subset of patients do
not have clinical or histolo...
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
(GERD) continues to be among the most common diseases seen by
gastroenterologists, surgeons, and primary care physicians. The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) recently
released an updated guideline on diagnosis and management of GERD which was
published by the American Journal of
Gastroenterology. In t...
Acute
upper gastrointestinal bleeding (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. In
Western countries, its incidence was estimated to be over 100 cases per 100 000
adults per year. Fortunately, the mortality rates of AUGIB have decreased over
the past few decades, largely attributable to improvements in endoscopic and
pharmacological therapies...