Featured
GERD is associated with substantial
reductions in subjective well-being, lower work productivity, and increased
healthcare use. The GERD in the Asia Pacific Survey (GAPS) found that GERD had
a negative impact on well-being for 94% of respondents in terms of stress (68%
of respondents), restrictions to daily activities (50%), and reduced wor...
A Systematic Review and
Meta-analysisGastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive
disorder resulting from the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus that
is often accompanied by troublesome symptoms of heartburn, acid regurgitation,
or other extra-esophageal symptoms such as chest pain, chronic cough,
hoarseness or glob...
TAKE-HOME MESSAGEAbout 80%
of pregnant women suffer from gestational reflux disease. Most
interventions are based on a “step-up” approach that begins with lifestyle
modifications. If the
symptoms persist despite lifestyle modification, a medical intervention can be
considered.
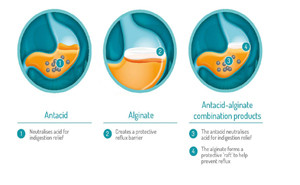
Antacids,
alginates and sucralfate are the first-line t...
The American Journal of
Gastroenterology
Gastroesophageal
reflux disease (GERD) continues to be among the most common diseases seen by
gastroenterologists, surgeons, and primary care physicians.
GERD is
the condition in which the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus
results in symptoms and/or complications. GERD is defined b...
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
This review presents best practice
advice statements to help healthcare providers in the treatment of patients
with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
To optimize care and response,
diagnostic testing should be personalized and management should be tailored to
the ind...
Proton
pump inhibitors (PPIs) are among the most commonly used medications in the
world. Developed for the treatment and prevention of acid-mediated upper
gastrointestinal conditions, these agents are being used increasingly for
indications where their benefits are less certain.
PPI over prescription
imposes an economic cost and contri...
Key Information
In the last decade, gastro-esophageal
reflux disease (GERD) and its complications of Barrett's oesophagus and
oesophageal adenocarcinoma are increasingly prevalent, especially in Asia. The
rise in GERD among Asians is largely attributed to a recent increase in the
prevalence of obesity.
Physiological dysfunction of the...
Heartburn is a cardinal symptom of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
(GERD) and is among the most common patient complaints encountered by physicians.
TAKE HOME MESSAGE:
This study compared the effect of Antacid & Alginate Liquid to an antacid
in controlling post-prandial acid reflux in GERD patients.
The current investigation demons...
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
The authors of this meta-analysis evaluated the
efficacy of alginate-containing compounds for the treatment of
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms. The odds of resolution of
GERD symptoms was significantly greater with alginate-based therapies than
with placebo or antacids. Alginate therap...
The management of gastroesophageal
reflux disease (GERD) has been revolutionized with the development of proton
pump inhibitors (PPIs). Unfortunately, due to the inherent pharmacokinetic and
pharmacodynamic profiles of conventional PPIs, many patients continue to suffer
from symptoms related to GERD despite appropriate use of PPIs.
Curr...
Antacids neutralize gastric acid
and are, broadly used in the
treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in adults. They are
utilized for more than 2,000 years, though evidence of the effectiveness and
safety is limited in infants [1]. Antacids have an effect on the short-term
relief of heartburn and the healing of esophagitis. Charac...
The American Journal of GastroenterologyTAKE-HOME MESSAGE
In a study evaluating sleep position and nocturnal
gastroesophageal reflux, the sleep positions of 57 individuals referred
for ambulatory pH impedance were measured and analyzed. The left lateral
position was associated with significantly shorter acid exposure time than...