Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19 (P-1)
FDA Authorizes Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19. The U.S. FDA issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the investigational monoclonal antibody therapy for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adult and pediatric patients.
Doctors Liked to Read More
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-made proteins that mimic the immune system’s ability to fight off harmful antigens such as viruses.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for Bamlanivimab and Casirivimab/Imdevimab to be administered together for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients (12 years of age or older weighing at least 40 kilograms) with positive results of direct SARS-CoV-2 viral testing and who are at high risk for progressing to severe COVID-19. This includes those who are 65 years of age or older or who have certain chronic medical conditions.
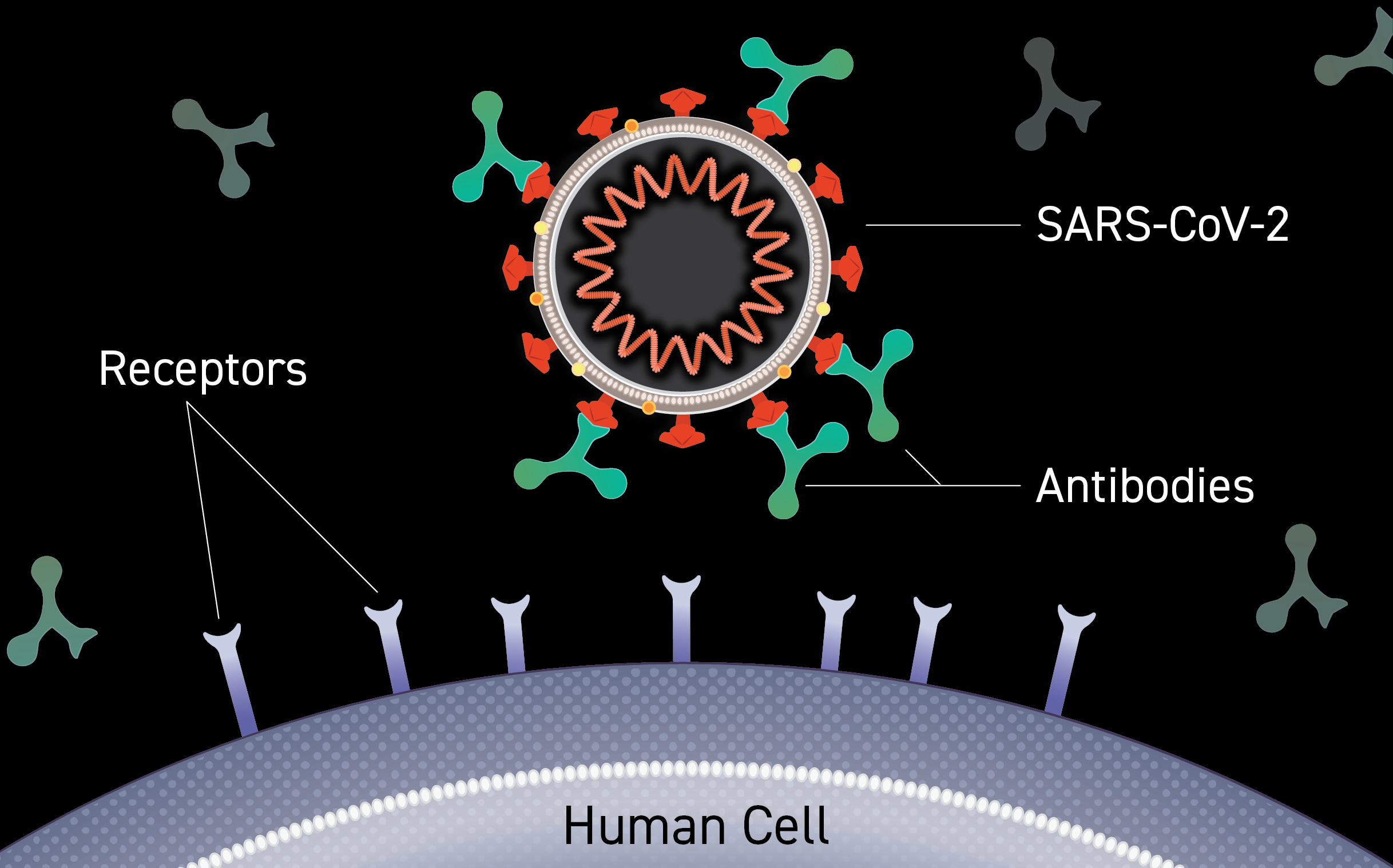
These are monoclonal antibody that is specifically directed against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, designed to block the virus’ attachment and entry into human cells.
Monoclonal antibody binds to the receptor binding domain of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, blocking the spike protein’s attachment to the human ACE2 receptor.
MAbs must be given by intravenous (IV) infusion. Therefore, mAbs
may be administered only in settings in which health care providers have
immediate access to medications to treat severe infusion reactions, such as
allergic reaction, and the ability to activate the emergency medical system, as
necessary.
During Phase 1 of distribution, mAbs are being shipped to hospitals and hospital-affiliated locations. Infusions may be administered only in settings in which health care providers have immediate access to medications to treat a severe infusion reaction, such as allergic reactions, and the ability to activate the emergency medical system, as necessary.
Since mAbs are indicated for patients in the early stages of COVID-19 illness who are infectious, locations must take into account the need to separate patients receiving mAbs from patients receiving other types of infusions who are vulnerable to infection (e.g., chemotherapy). Hospitals have flexibility in determining where to administer infusions of mAbs, as long as these conditions are met.
A clinical trial called BLAZE-1 studied bamlanivimab for the treatment of adult patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 who were not hospitalized. Bamlanivimab was shown to decrease hospitalizations and ER visits and to decrease patients’ viral load compared to those who got a placebo. Among patients who were at high risk for disease progression, hospitalizations and emergency room visits occurred in 3% of bamlanivimab-treated patients, compared to 10% in placebo-treated patients. For more information, see SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody LY-CoV555 in Outpatients with Covid-19. Clinical trials are continuing to study bamlanivimab for patients with COVID-19.
Another clinical trial studied the combination of casirivimab and indevimab for the treatment of adult patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 who were not hospitalized. Similar to bamlanivimab, casirivimab/indevimab was also shown to decrease hospitalizations and ER visits and to decrease patients’ viral load compared to placebo. In patients who were at high risk for disease progression, hospitalizations and emergency room visits occurred in 3% of casirivimab/indevimab-treated patients, compared to 9% in placebo-treated patients. Clinical trials are continuing to study casirivimab/indevimab for patients with COVID-19.
https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/coronavirus/hcp/bamfaq.html#where1
https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-monoclonal-antibody-treatment-covid-19
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2774326
https://www.lilly.com/news/media/media-kits/bamlanivimab-covid19



Comments
You must login to write comment