Hypertension Management Guidelines
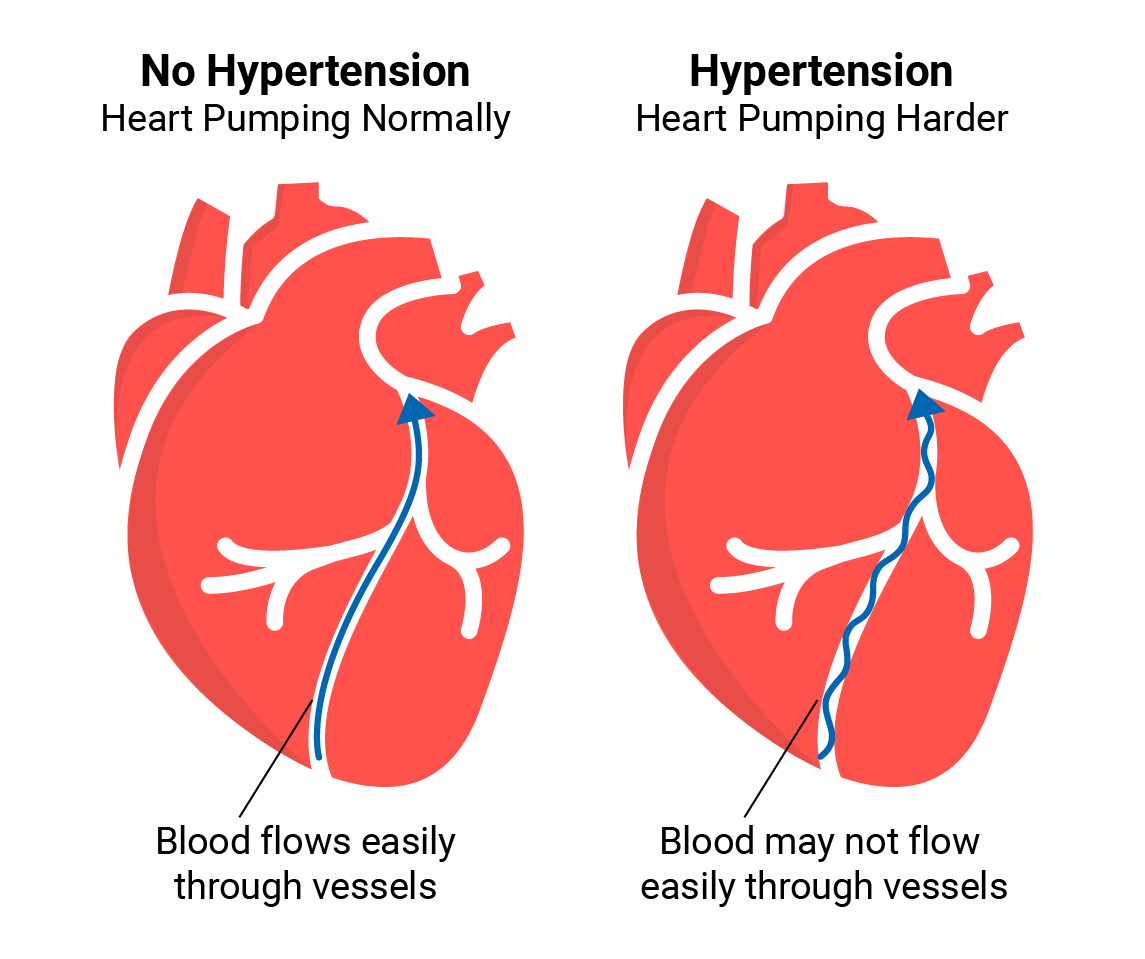
Management of hypertension
Many guidelines exist for the management of hypertension. Most groups, including the JNC, the American Diabetes Associate (ADA), and the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (AHA/ASA) recommend lifestyle modification as the first step in managing hypertension.
Lifestyle modifications
JNC 7 recommendations to lower BP and decrease
cardiovascular disease risk include the following, with greater results
achieved when 2 or more lifestyle modifications are combined:
- Weight
loss (range of approximate systolic BP reduction [SBP], 5-20 mm Hg per 10
kg)
- Limit
alcohol intake to no more than 1 oz (30 mL) of ethanol per day for men or
0.5 oz (15 mL) of ethanol per day for women and people of lighter weight
(range of approximate SBP reduction, 2-4 mm Hg)
- Reduce
sodium intake to no more than 100 mmol/day (2.4 g sodium or 6 g sodium
chloride; range of approximate SBP reduction, 2-8 mm Hg)
- Maintain
adequate intake of dietary potassium (approximately 90 mmol/day)
- Maintain
adequate intake of dietary calcium and magnesium for general health
- Stop
smoking and reduce intake of dietary saturated fat and cholesterol for
overall cardiovascular health
- Engage in aerobic exercise at least 30 minutes daily for most days (range of approximate SBP reduction, 4-9 mm Hg)
The AHA/ASA recommends a diet that is low in sodium, is high in potassium, and promotes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products for reducing BP and lowering the risk of stroke. Other recommendations include increasing physical activity (30 minutes or more of moderate-intensity activity on a daily basis) and losing weight (for overweight and obese persons).
Treatment Recommendations
The following are drug class recommendations for compelling
indications based on various clinical trials:
- Heart
failure: Diuretic, beta-blocker, ACE inhibitor/ARB, aldosterone
antagonist
- Following
myocardial infarction: Beta-blocker, ACE inhibitor
- Diabetes: ACE
inhibitor/ARB
- Chronic
kidney disease: ACE inhibitor/ARB
American Society of
Hypertension/International Society of Hypertension
Joint guidelines were issued by the American Society of Hypertension and
the International Society of Hypertension (ASH/ISH)
|
Major Medical Condition |
First-line Drugs |
Added 2nd Drug |
Added 3rd Drug |
|
|
Diabetes (white and other non-African ancestry) |
ARB or ACEI |
CCB or thiazide diuretic |
Alternative 2nd drug (CCB or thiazide diuretic) |
|
|
Chronic kidney disease |
ARB or ACEI |
CCB or thiazide diuretic |
Alternative 2nd drug (CCB or thiazide diuretic) |
|
|
Coronary artery disease |
Beta-blocker plus ARB or ACEI |
CCB or thiazide diuretic |
Alternative 2nd drug (CCB or thiazide diuretic) |
|
|
Stroke |
ACEI or ARB |
CCB or thiazide diuretic |
Alternative 2nd drug (CCB or thiazide diuretic) |
|
|
Symptomatic heart failure |
Beta-blocker plus ARB or ACEI plus diuretic plus spironolactone regardless of BP; CCB can be added if needed for BP control |
|||
|
ACEI = angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB = angiotensin receptor blocker; BP = blood pressure; CCB = calcium channel blocker. |
||||
Doctors Liked to Read More
2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA
Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High
Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of
Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice
Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018; 71:e127-e248.
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/241381-guidelines
https://www.guidelines.co.uk/cardiovascular/nice-hypertension-guideline/454934.article
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng136
Note: For informational purposes
only. Consult your textbook for advising your patients.



Comments
You must login to write comment