Current Guidelines for Insulin Initiation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin Initiation in Patients
with Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin initiation and titration is
a challenge for many primary care providers (PCPs) involved in the treatment of
patients with type 2 diabetes.
What are ADA recommendations?
The early introduction of insulin should be considered -
· if
there is evidence of ongoing catabolism (weight loss),
· if
symptoms of hyperglycemia are present, or
· when
A1C levels (>10% [86 mmol/mol]) or
· blood glucose levels (≥300 mg/dL [16.7 mmol/L]) are very high.
If the A1C target is not achieved
after approximately 3 months, Metformin can be combined with
any other oral hypoglycemic agent or Basal insulin; the choice of
which agent to add is based on drug-specific effects and patient factors.
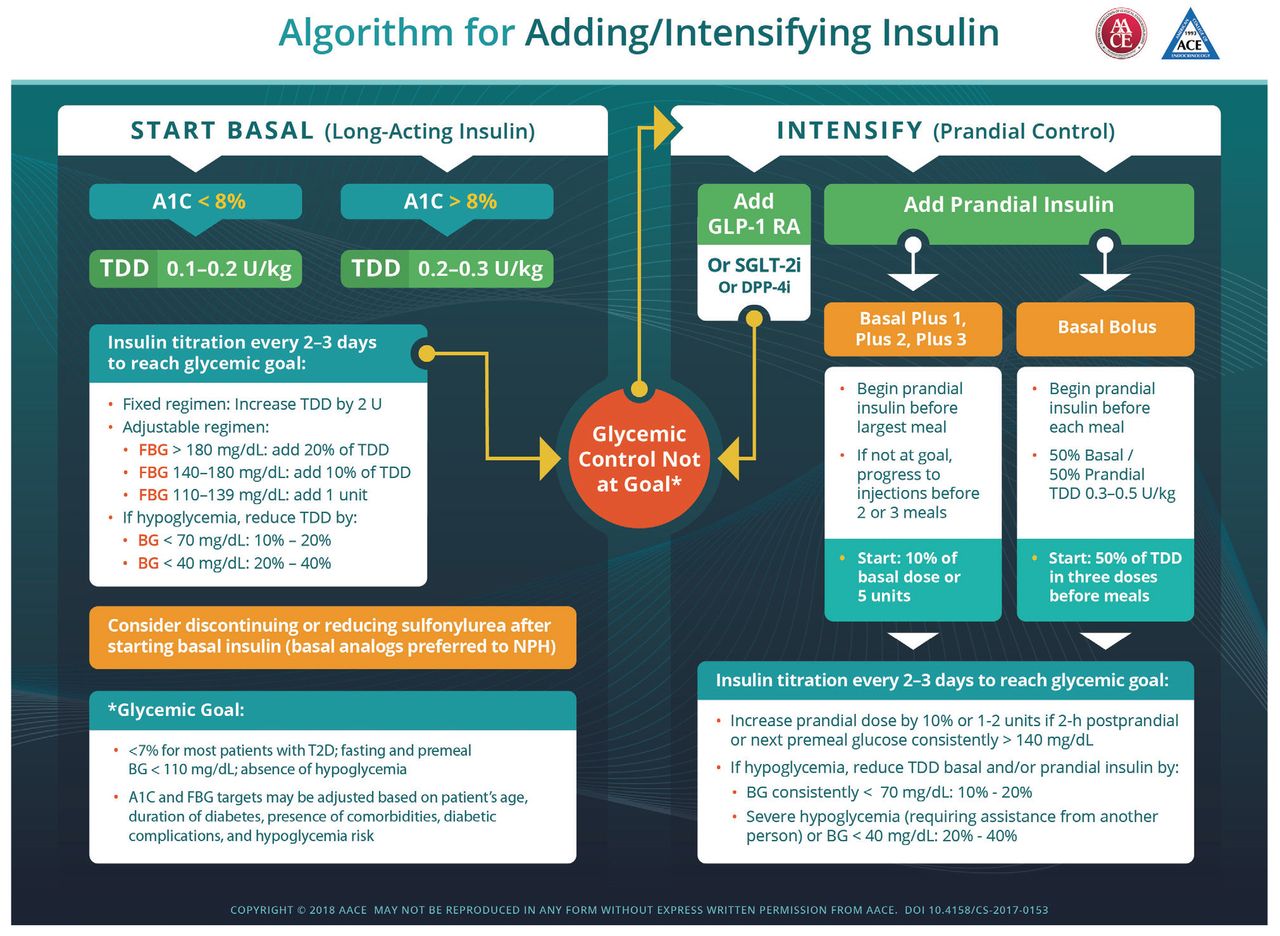
· Control of fasting glucose can be achieved with human Intermediate acting NPH basal insulin (Insulin Human N) or a Long-acting basal insulin analog (Glargine, Detemir, Degludec).
Note: Initiation of basal insulin at 10 units/day or 0.1–0.2 units/kg/day, adjusted by 10–15% or 2–4 units once or twice weekly to reach a target fasting plasma glucose (FPG) in patients whose A1C remains uncontrolled after >3 months of triple combination therapy.
Doctors Liked to Read More
Three regimen options should be considered:
- Regimen 1: Administer
one rapid-acting or short acting prandial insulin (Insulin Human R, Aspart, Lispro, Glulisine) injection before the meal with the
greatest carbohydrate content; if the glycemic target is not met, progress
to two or more rapid-acting insulin injections before meals (basal-bolus
regimen).
- Regimen 2: Add
a GLP-1 receptor agonist (Liraglutide, Semaglutide).If target A1C remains unmet or the
regimen is not tolerated, patients may discontinue the GLP-1 receptor
agonist and switch to regimen 1 or 3.
- Regimen 3: Replace
basal insulin with premixed insulin at a 75/25, 70/30, or
50/50 mix twice (usually before breakfast or dinner) or thrice daily
(before breakfast, lunch, and dinner).
Note: Basal
insulin and GLP-1 receptor agonists should be discontinued before initiating
premixed insulin.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › articles › PMC2811456
Note: For informational purposes only. Consult your textbook for advising your patients.




Comments
You must login to write comment