Drug-highlights
eClinicalMedicine Journal: The LANCET: Published on December, 2022Gram-negative bacteremia is common
in both community and health care settings, with a significant increase in
incidence described for some Gram-negative bacteria in recent years.Prolonged duration of antibiotic
therapy for such common infections may lead to increased resistance em...
The New England Journal of Medicine: Published on December, 2022Hypertension increases the risk of complications and death
from cardiovascular disease. Thiazide diuretics are first-line
antihypertensive agents that lower blood pressure and prevent adverse
cardiovascular outcomes. Early studies suggested that chlorthalidone was superior to
hydro...
The New England Journal of Medicine:
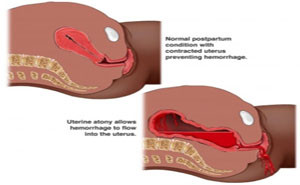
Postpartum
hemorrhage is a major cause of maternal death and severe maternal complications
after childbirth. Currently, the prophylactic administration of a uterotonic
agent immediately after delivery is recommended for all women as the only
procedure that has been proved to reduce rates of postpartum...
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) & The New England Journal of
Medicine (NEJM):
Key Prescribing Notes:
Perioperative bleeding is common
complications in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery, is associated with
increased morbidity and mortality.
The goal of the POISE-3 trial was
to determine whether tranexamic acid, when u...
Cefuroxime is a 2nd generation cephalosporin group of broad-spectrum β-lactam
antibiotic.Clavulanic acid is a
beta lactamase inhibitor used to enhance the effectiveness of beta lactam
antibiotics.Cefuroxime and Clavulanic Acid: A
combination of cefuroxime and ß -lactamase inhibitor (Clavulanic acid) for the
treatment of various bacterial infec...
Diabetes, a silent killer, is a
leading cause of neuropathy. Around 50% of diabetic patients develop peripheral
neuropathy in 25 years. Painful diabetic neuropathy manifests as burning,
excruciating, stabbing or intractable type of pain or presents with tingling or
numbness. The pathophysiology of this
condition is due to primarily metabolic a...
Fig: PharyngotonsillitisTAKE-HOME MESSAGE
It is important to optimize existing antibiotics in
view of increasing antimicrobial resistance and paucity of new drugs in
this class. One of the most common infections treated by primary care
physicians is pharyngotonsillitis, and it is associated with a significant
proportion of...
Insulin Initiation in Patients
with Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin initiation and titration is
a challenge for many primary care providers (PCPs) involved in the treatment of
patients with type 2 diabetes. What are ADA recommendations?The early introduction of insulin should be considered -· if
there is evidence of ongoing catabolism (weight...
To reduce the development of
drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of antibiotics and other
antibacterial drugs, antibiotics should be used only to treat or prevent
infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible
bacteria.
When culture and susceptibility
information are available, they should b...
Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic disorder of the
digestive system caused by the lower esophageal sphincter not closing properly.
This can allow stomach acid, bile into esophagus, causing inflammation and, in
some cases, tooth erosion.
Heartburn and acid regurgitation
are the main symptoms of GERD, though some people have...
Antibiotics treatment for bacterial
pneumonia in adults in hospital
Antibiotic management of
suspected or confirmed bacterial pneumonia in adults in hospital during the
COVID-19 pandemic. This includes people presenting to hospital with moderate to
severe community-acquired pneumonia and people who develop pneumonia while in
hospital.COVID...
A study published Oct. 12
in the Annals of Internal Medicine that compared three types of direct oral
anticoagulants (DOACs) found that rivaroxaban was associated with a much higher
risk of overall and major gastrointestinal bleeding than apixaban or
dabigatran, according to a study. Other studies yield similar results.The researchers found
th...