Drugs-for-fungal-infections-anti-fungal
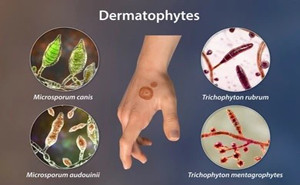
International Journal of Scientific Study (IJSS): May, 2020Superficial fungal infections are
caused by dermatophytes, non-dermatophytic molds, and commensal yeasts. According to published literature, the global prevalence rate of superficial
mycotic infection has been found to be 20–25%. The recent prevalence of
dermatophytosis in India ranges f...
JAMA Dermatology: Published November, 2022Despite the widespread use of
nutritional supplements and dietary interventions for treating hair loss, the
safety and effectiveness of available products remain unclear.The aim
of the study is to evaluate and compile the findings of all dietary
and nutritional interventions for treatment of hair loss a...
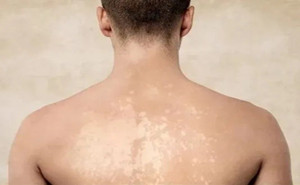
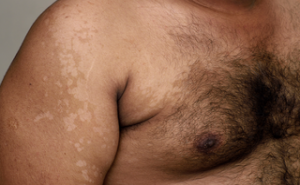
Pityriasis versicolor (PV) also
known as tinea versicolor, which is chronic and superficial fungal skin disease
caused by Malassezia yeasts. A permanent cure may difficult to achieve and this
may explain the long-term nature of the disease. Consequently, a preventive
treatment regimen may help to prevent the recurrence of pityriasis versicolor....
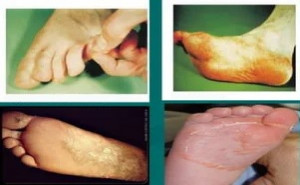
The British Journal of DermatologyDermatophytic infections have
undergone unprecedented changes in India in the recent past. Oral antifungal drugs are
considered to have a high cure rate in tinea corporis, tinea cruris and tinea
faciei.Clinical trials to find out the
effectiveness of the four main oral antifungal drugs are lacking.Authors teste...
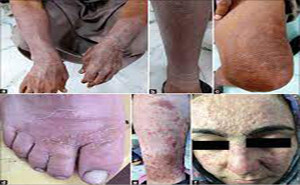
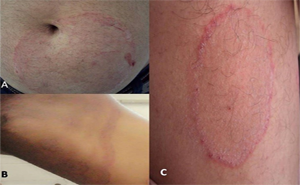
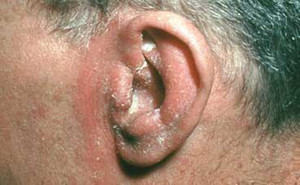
Superficial fungal infections are primarily caused by
dermatophytes, Candida spp, and Malassezia species affects 20%–25% of the
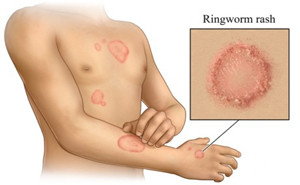
world’s population.The lesion of dermatophytosis is present with an annular or
ring-shaped red scaly plaque with central clearing, often associated with
severe pruritus.Systemic or topical antifungal drugs are used as...
Clinicians should be more judicious in prescribing or
recommending oral or topical antifungal therapy.Given the limited selection of antifungals, it is paramount
to mitigate resistant cases. Mitigation proposals include:·
good
skin hygiene,· &nb...
International Journal of Research in Dermatology: Published
on February, 2021Dermatophytic infections are the
most prevalent fungal infections, which affect majority of the global
population. Indian climate, especially the hot and humid conditions contribute
majorly to dermatophytosis. Azoles are the most commonly used
antifungal agents due t...
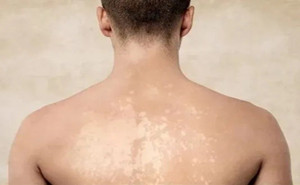
Pityriasis versicolor (PV), also
known as tinea versicolor, is caused by Malassezia species.
This condition is one of the most common superficial fungal infections
worldwide. This may be triggered by various
factors, including humidity and high temperature, hyperhidrosis, familial
susceptibility, and immunosuppression. Consequently,...
Tinea (pityriasis) versicolor is a
superficial fungal infection and one of the most commonly found pigmentary
disorders of skin caused by the yeast Malassezia. Multiple topical as well as
systemic therapies are available for treatment. Systemic therapies are used for
extensive disease, frequent relapse or where topical agents have failed. TAKE...
PubMed: Published on April 2022Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is a
common inflammatory skin disease, which is particularly prevalent in older
adults, presenting with papulosquamous morphology in areas rich in sebaceous
glands, particularly the scalp, face, and body folds.PathogenesisWhile a specific cause of
seborrheic dermatitis remains largely un...
The Journal of Dermatology:Luliconazole Cream, 1% is an azole
antifungal indicated for the topical treatment of interdigital tinea pedis,
tinea cruris, and tinea corporis caused by the organisms Trichophyton rubrum
and Epidermophyton floccosum.TAKE HOME MESSAGES: Authors evaluated the efficacy and
safety of luliconazole cream 1% in the treatmen...
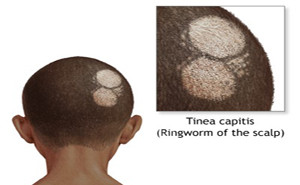
European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology: Published
on July, 2018Tinea capitis is the most common
cutaneous fungal infection in children.TAKE HOME MESSAGEThis review aims to evaluate the
differences that exist between medications for the treatment of tinea capitis,
to determine whether there are any significant adverse effects associated...