Featured
Ketoconazole
is in a class of antifungal medications called imidazoles. It works by inhibiting
the growth of fungi that cause the infection.
Topical
ketoconazole is indicated for the treatment of cutaneous candidosis (including
vulvitis), tinea (pityriasis) versicolor and seborrhoeic dermatitis caused by
Malassezia (previously called Pi...
International Journal of Research in Dermatology: March,
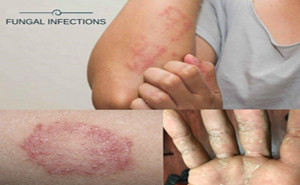
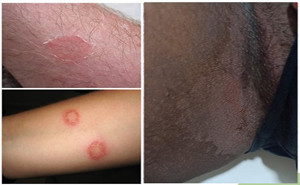
2022Tinea caused by trichophyton, microsporum, and epidermophyton is the most common fungal infection affecting 20–25% population globally, with varying geographic distribution.Due to Bangladesh’s hot and humid cli...
The prevalence of superficial
fungal infections across the globe is increasing from 20-25%. Superficial
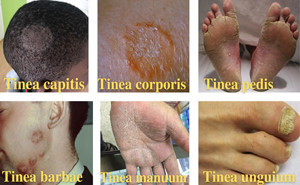
infections are mostly caused by dermatophytes. Depending on the site affected,
the dermatophytes are clinically classified as Tinea capitis (head), Tinea
faciei (face), Tinea barbae (beard), Tinea manus (hand), Tinea corporis (body),
Tinea c...
There has been a significant
increase in the incidence of chronic, relapsing, recurrent cases of superficial
dermatophytosis in India that are also often unresponsive to conventional drugs
and doses of recommended antifungal treatment. Almost 15– 20% of the outpatient
department cases are those of chronic dermatophytosis. Recurrences and relaps...
Mycoses Journal: Published on April 2021Dermatomycoses of zoophilic origin,
especially those caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes, often pose considerable
therapeutic problems. This is reflected in the growing number of strains of
this species with resistance to terbinafine caused by a mutation in the
squalene epoxidase (SQLE) gene. TAKE HOME...
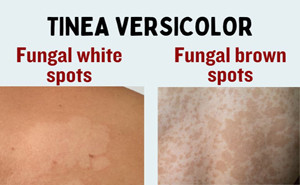
PubMed Central: November, 2022Tinea versicolor is a common superficial fungal infection of
the skin with various clinical manifestations. This review aims to familiarize
physicians with the clinical features, diagnosis and management of tinea
versicolor.Tinea versicolor is caused by Malassezia species,
notably M. globosa, M....
Infection and Drug Resistance Journal:Tinea is superficial fungal infections typically caused by
dermatophytes.Superficial fungal infections are widespread, with an
estimated worldwide prevalence of 20%–25%, and include tinea pedis (athlete’s
foot), tinea cruris (jock itch), and tinea corporis (ringworm), among othersTopical allylamine (terbinaf...
Indian Journal of Pharmacology: Published: May, 2019Dermatophytic infections are the
common fungal infections aggravated by hot and humid climate. Terbinafine and Itraconazole
are commonly used oral antifungal agents for the same. However, resistance to
these drugs is being seen increasingly when used in the conventional doses and
duration. In...
Principles of TherapyTopical AntifungalsTopical medications have better
pharmacokinetics than their systemic counterparts. Hence, the combination is
expected to have better mycological clearance than systemic and topical alone. The combination should be from
different groups for wide coverage and also to prevent the emergence of resistance.
Dru...
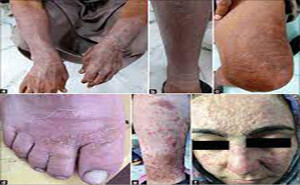
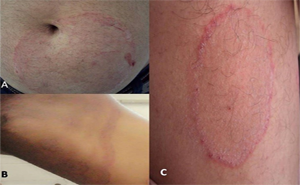
Superficial fungal infections are primarily caused by
dermatophytes, Candida spp, and Malassezia species affects 20%–25% of the
world’s population.The lesion of dermatophytosis is present with an annular or
ring-shaped red scaly plaque with central clearing, often associated with
severe pruritus.Systemic or topical antifungal drugs are used as...
International Journal of Research in Dermatology: Published
on February, 2021Dermatophytic infections are the
most prevalent fungal infections, which affect majority of the global
population. Indian climate, especially the hot and humid conditions contribute
majorly to dermatophytosis. Azoles are the most commonly used
antifungal agents due t...
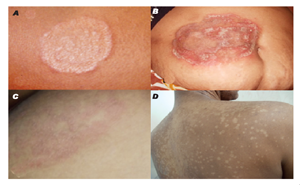
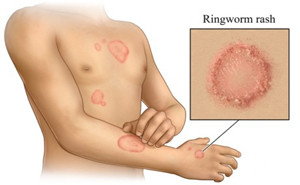
European Journal of Molecular & Clinical Medicine: Published
on 2020Superficial infection caused by a
dermatophyte is termed dermatophytosis or ringworm. They are all moulds
belonging to three asexual genera: microsporum, trichophyton and
epidermophyton.Depending upon the site of
infection, dermatophyte infection can be classified as...