Posted by ACI Limited
The Pediatric Infectious
Disease Journal:
Clostridium difficile is an important cause of
antibiotic-associated diarrhea and the most widely recognized diarrheal
pathogen acquired in healthcare settings.
Antibiotic or gastric acid suppressant exposure, gastrointestinal feeding
devices, and certain medical conditions, such as malign...
BioMed Central (BMC) Gastroenterology Journal:
Gastroesophageal
reflux disease (GERD) is one the most common medical complaints in
pregnant women. Its prevalence has been reported to reach as high as 80% in
certain populations. The prevalence of GERD is also increased as pregnancy
progresses from the first to third trimester. Some women...
The British Medical Journal (BMJ):
British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and British
Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (BSPGHAN)
joint consensus guidelines
Eosinophilic oesophagitis is a condition characterised by
symptoms of dysphagia and/or food impaction in adults, and feeding problems,
abdominal...
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
The authors of this meta-analysis evaluated the
efficacy of alginate-containing compounds for the treatment of
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms. The odds of resolution of
GERD symptoms was significantly greater with alginate-based therapies than
with placebo or antacids. Alginate therap...
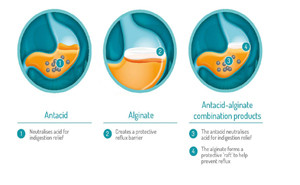
Antacids neutralize gastric acid
and are, broadly used in the
treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in adults. They are
utilized for more than 2,000 years, though evidence of the effectiveness and
safety is limited in infants [1]. Antacids have an effect on the short-term
relief of heartburn and the healing of esophagitis. Charac...
COVID-19 Update:In light of the most recent
information and data available, today, the FDA revised the authorizations for
two monoclonal antibody treatments – bamlanivimab
and etesevimab (administered together) and casirivimab and imdevimab – to limit their use to only when the
patient is likely to have been infected with or exposed to a varian...
Reflux disease is a chronic and
progressive condition. Treatment options depend on the disease stage. The
disease stage is determined by the severity of reflux into the esophagus. This
in turns depends on how frequent and how long are the reflux episodes. GERD is also associated with a
spectrum of symptoms that ranges from mild heartburn to sev...
Medical management of GERD mainly
uses proton pump inhibitors. Alginates plus Antacids also have proven efficacy.
Tolerance and safety were good and comparable in both groups.Alginates plus Antacids was
non-inferior to omeprazole in achieving a 24-h heartburn-free period in
moderate episodic heartburn, and is a relevant effective alternative tr...
Association between COVID-19 and
Myocarditis Using Hospital-Based Administrative Data — United States, March
2020–January 2021
Viral infections are a common
cause of myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium) that can
result in hospitalization, heart failure, and sudden death. Emerging data
suggest an association between...
A Double Action Antacid &
Alginate Liquid was more effective than an antacid in controlling postprandial
esophageal acid exposure in GERD patients. This suggests that this main
effectiveness related to its co-localization with and
displacement/neutralization of the post-prandial acid pocket, rather than
preventing reflux.Heartburn is...