Posted by Nuvista Pharma Ltd
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic,
progressive, fibroinflammatory lung disease associated with increased morbidity
and mortality. As its name suggests, the exact cause of the disease is not
known. However, some genetic and environmental factors have been
observed concurrently with the condition and are considered potential etiolo...
The American Journal of
Gastroenterology
GERD MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
Management
of GERD requires a multifaceted approach, taking into account the symptom
presentation, endoscopic findings, and likely physiological abnormalities.
Medical
management includes lifestyle modifications and pharmacologic therapy,
principally with medication...
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an
immune/antigen-mediated, progressive fibrostenotic disease characterized by
symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and abnormal eosinophilic infiltration in
the esophagus. Despite treatment modalities of
dietary antigen elimination or Topical corticosteroids, a subset of patients do
not have clinical or histolo...
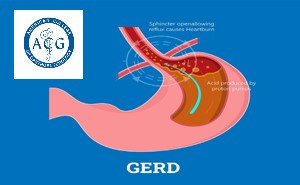
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
(GERD) continues to be among the most common diseases seen by
gastroenterologists, surgeons, and primary care physicians. The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) recently
released an updated guideline on diagnosis and management of GERD which was
published by the American Journal of
Gastroenterology. In t...
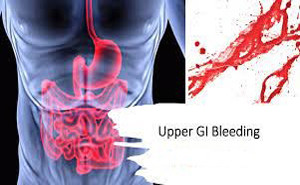
Acute
upper gastrointestinal bleeding (AUGIB) is a common medical emergency. In
Western countries, its incidence was estimated to be over 100 cases per 100 000
adults per year. Fortunately, the mortality rates of AUGIB have decreased over
the past few decades, largely attributable to improvements in endoscopic and
pharmacological therapies...
The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal:
Take Home Message:
Diarrheal
disease is a leading cause of childhood morbidity and mortality globally.
Rotavirus is the leading cause of
vaccine-preventable diarrhea among children under 5 and is associated with
approximately 28% of diarrheal deaths. The highest burden of severe disease and
d...
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
(GERD) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) are two pathological conditions
often strictly related, even if a clear relationship of causality has not been
demonstrated.
GERD is a frequent comorbidity in
IPF patients, as demonstrated using combined multichannel intraluminal
impedance-pH, despite being...
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics:
Functional dyspepsia is
characterised by troublesome early satiety, fullness, or epigastric pain or
burning. It can easily be overlooked as the symptoms overlap with
gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and irritable bowel syndrome.
It affects 10% of the population
and is more prevalent in women....
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) are widely considered the
mainstay of medical treatment for GERD. Multiple publications have raised questions about adverse
events, raising doubts about the safety of long-term use and increasing concern
about overprescribing of PPIs. This guideline provides updated, evidence-based recommendations and
practical...
Indian Journal of Gastroenterology: Published:
30 June 2022
TAKE HOME MESSAGE:
Nocturnal acid breakthrough (NAB)
may differ based on duration of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) action and Helicobacter
pylori (H. pylori) infection; NAB may influence esophageal
acidification (EA) and mucosal damage.
Dexlansoprazole, a long-acting PPI,...
GERD is associated with substantial
reductions in subjective well-being, lower work productivity, and increased
healthcare use. The GERD in the Asia Pacific Survey (GAPS) found that GERD had
a negative impact on well-being for 94% of respondents in terms of stress (68%
of respondents), restrictions to daily activities (50%), and reduced wor...
The management of gastroesophageal
reflux disease (GERD) has been revolutionized with the development of proton
pump inhibitors (PPIs). Unfortunately, due to the inherent pharmacokinetic and
pharmacodynamic profiles of conventional PPIs, many patients continue to suffer
from symptoms related to GERD despite appropriate use of PPIs.
Curr...