Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): What Doctor’s need to know
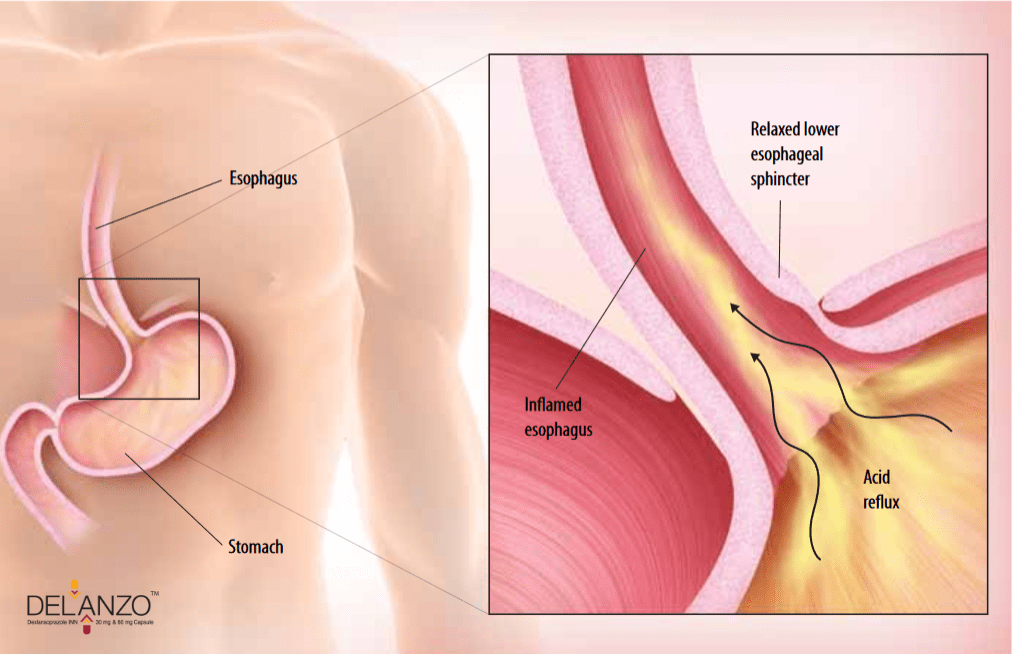
GERD is a chronic disorder of the digestive system caused by the lower esophageal sphincter not closing properly. This can allow gastric acid, bile into esophagus, causing inflammation and, in some cases, tooth erosion.
GERD occurs more commonly in individuals who are:
- Overweight or obese because of increased pressure on the abdomen.
- Pregnant women due to increase pressure on lower abdomen.
- Taking medications, including some asthma medications, calcium channel blockers, antihistamines, sedatives, and antidepressants.
- Smoking and being exposed to second-hand smoke.
Note: GERD is almost never caused by the production of too much acid. It is caused by abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus.
Doctors Liked to Read More
Typical esophageal symptoms include
the following:
- Heartburn
- Regurgitation
- Dysphagia
Abnormal reflux can cause atypical
(extraesophageal) symptoms, such as the following:
- Coughing and/or wheezing
- Hoarseness, sore throat
- Otitis media
- Noncardiac chest pain
- Enamel erosion or other dental manifestations
A history of nausea, vomiting, or
regurgitation should alert the physician to evaluate for delayed gastric
emptying.
Treatment of GERD involves a
stepwise approach. The goals are to control symptoms, to heal esophagitis, and
to prevent recurrent esophagitis or other complications.
The treatment is based on -
(1) Lifestyle modification and
(2) Control of gastric acid
secretion through medical therapy with Antacids or H2 receptor blockers or
PPIs or Surgical treatment with corrective anti-reflux surgery.
Note: Among the
PPI, Dexlansoprazole Delayed Release capsule has been shown to
be highly efficacious in healing erosive esophagitis, maintaining healed
esophageal mucosa and controlling symptoms of patients with non-erosive reflux
disease (NERD) and highly effective in improving nocturnal heartburn associated
with GERD and bothersome regurgitation.
https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gastrointestinal-disorders/esophageal-and-swallowing-disorders/gastroesophageal-reflux-disease-gerd? query=Gastroesophageal%20Reflux%20Disease%20
(GERD)
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/gastroesophageal-reflux-disease-gerd
https://www.verywellhealth.com/gastroesophogeal-reflux-disease-gerd-5092827
https://gi.org/topics/acid-reflux/
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/176595-clinical
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/gastroesophageal-reflux
https://journals.lww.com/ajg/Fulltext/2013/03000/Guidelines_for_the_Diagnosis_and_Management_of.6.aspx
Note: For
informational purposes only. Consult your textbook for advising your patients.






Comments
You must login to write comment