Asthma & Covid 19: What Doctor’s Need to Know
The COVID-19 pandemic has presented challenges in management and
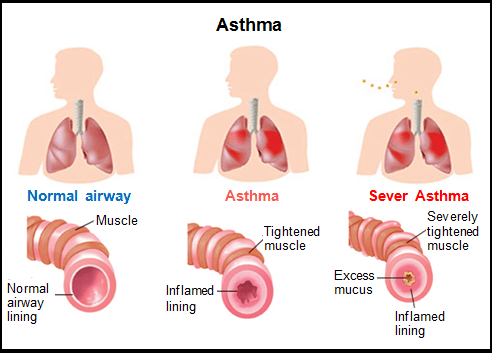
follow-up in common respiratory diseases such as asthma.
This review will discuss the current recommendations regarding asthma and
COVID-19 based on best available evidence at this time.
Doctors Liked to Read More

In light of this unique medical
challenge by COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians are faced with case-by-case based
decisions to implement or continue current asthma therapy and in particular the
leukotriene inhibitor, Montelukast.
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are
a common and effective first line treatment for control of asthma.
Leukotriene receptor antagonists such
as Montelukast act as an effective add on therapy for asthma control by
promoting anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator effects in the respiratory
tract.
Treatment of asthma maintenance
with montelukast should be continued according to current national and
international asthma treatment guidelines1.
The investigation revealed that
Montelukast decreased the rate of COVID 19 infection in elderly patients with
severe asthma2.
·
Of the hospitalized patients with Covid-19,
those taking Montelukast, did not need respiratory therapy or multidrug
antiviral treatment.
·
Additionally, it was found that Covid-19
positive patients that were treated with Montelukast experienced significantly
fewer events of clinical deterioration that those not receiving the treatment.
It may have a role in the
decreasing need for respiratory and multi drugs antiviral therapy in
hospitalized COVID-19 patients2.
Montelukast inhibits the
synthesis of leukotriene thereby decreasing airway inflammation and promoting
bronchodilation3.
Montelukast has been shown to
decrease both lung inflammation and cytokine release. Montelukast was also
shown to reduce eosinophilic inflammation in upper airway inflammatory disease
by inhibiting epithelial cell cytokine release and promoting eosinophil
survival.
Licskai, C, Yang, CL, Ducharme,
FM, et al. Addressing therapeutic questions to help Canadian physicians
optimize asthma management for their patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Can
J Respir Crit Care Sleep Med. 2020;4:73-76.
Bozek, A, Winterstein, J.
Montelukast’s ability to fight COVID-19 infection. J Asthma. 2020:1-2.
doi:10.1080/02770903.2020.1786112.
Gosens, R, Gross, N. The mode of
action of anticholinergics in asthma. Eur Respir J. 2018;52:1701247.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33173369/
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1179548420966242
Note: For informational
purposes only. Consult your textbook for advising your patients.




Comments
You must login to write comment