Featured
Journal of the American Medical
Association (JAMA)
SurgeryTranexamic
acid is an antifibrinolytic compound which inhibits fibrinolysis by blocking
the binding of plasminogen and plasmin to fibrin, thus preventing dissolution
of the haemostatic plug.
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
Question Is
intravenous administration of tranexamic acid associated wi...
The New England Journal of Medicine:
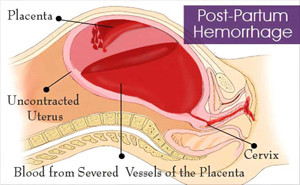
Postpartum
hemorrhage remains a leading cause of severe maternal complications and death worldwide.
Prophylactic administration of an uterotonic agent is recommended to reduce the
risk of postpartum hemorrhage. Tranexamic acid has emerged in the past decade
as another candidate drug to prevent blood l...
A meta-analysis of the randomized
controlled trials: The American
Journal of Emergency Medicine
Trauma remains a leading cause of
death worldwide, and the management of injured patients at risk for hemorrhage
has evolved over time.
Interventions provided to injured
patients during prehospital care, close to the time of injury, result...
Trauma is the leading cause of
death and disability worldwide. In both military and civilian settings, hemorrhage
remains the most common cause of preventable death after traumatic injury. In
recent years, there has been considerable interest in antifibrinolytic agents
for the prevention of hemorrhagic death in severe trauma patients.
T...
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) & The New England Journal of
Medicine (NEJM):
Key Prescribing Notes:
Perioperative bleeding is common
complications in patients undergoing noncardiac surgery, is associated with
increased morbidity and mortality.
The goal of the POISE-3 trial was
to determine whether tranexamic acid, when u...