Featured
APPROACH CONSIDERATIONS
The goal of treatment is to provide
adequate relief of pain. At a minimum, pain relief should be sufficient to
allow women to perform most, if not all, of their usual activities and to
reduce the productivity loss commonly associated with dysmenorrhea.
Treatment of primary dysmenorrhea
can be initiated empiric...
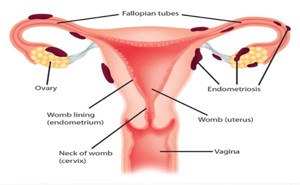
Obstetrics and Gynecology Journal: Published on October 2021Endometriosis affects 6–10% of reproductive-aged women and is
associated with significant morbidity.Clinical manifestations are broad and can include
dysmenorrhea, nonmenstrual pelvic pain, dyspareunia, dyschezia, and
infertility. The wide range of presentations hinder the ability...
Puberty menorrhagia is defined as excessive bleeding in amount (>80ml)
or in duration
(>7days) between menarche and
19 years of
age.The most common cause of puberty menorrhagia
is anovulatory cycles. Other causes include infection, bleeding disorders, and endoc...
Dysmenorrhea, or menstrual pain, is the most common menstrual
symptom among adolescent girls and young women. Most adolescents experiencing dysmenorrhea have primary
dysmenorrhea, defined as painful menstruation in the absence of pelvic
pathology. Primary dysmenorrhea characteristically begins when adolescents
attain ovulatory cycles, usually w...
The majority (70-93%) of adolescents have discomfort associated
with menstruation. Dysmenorrhea is the most common reason for missed school and
activities. Up to 20-40% report missed school due to dysmenorrhea, and 40%
report a negative effect on school performance and concentration. Adolescents
with severe dysmenorrhea have impaired qualit...