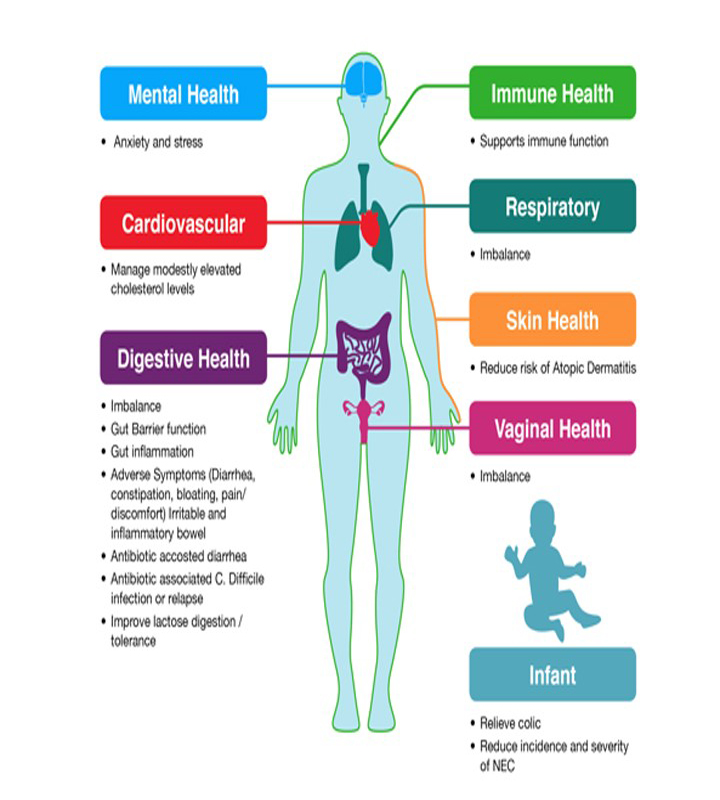
Recommendation of clinical use of Probiotics in Medical Text Books
Probiotics are living non-pathogenic microorganisms, which
when given in sufficient amounts should be
beneficial to host by improving its microbial balance in gut and participate in
the metabolism.
Probiotics uses are common and recommended in different text books.
Find out below beneficial effects of probiotics and what are covered in Medical Textbooks about Probiotics:
Doctors Liked to Read More
Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine, 22nd
Ed, Page-908, Fig 22.57
· For reducing IBS pain & bloating as spasmolytics and also as Probiotics, in capsule form, can be effective if taken for several months, although the optimum combination of bacterial strains and dose have yet to be clarified.
A range of complementary and
alternative therapies exist such as probiotics; most lack a good evidence base
but are popular and help some patients in IBS.
Harrison’s principles of internal medicine, 19th Ed,
P-263, 797, 1970
·
For IBS patients with
predominant gas and bloating, some
patients may benefit from probiotics and rifaximin treatment.
·
Therapies to
modify gut flora (non-absorbable antibiotics, probiotics) reduce gaseous
symptoms in some IBS patients.
·
Because altered
colonic flora may contribute to the pathogenesis of IBS, this has led to great interest in using
probiotics to naturally alter the flora.
·
A meta-analysis
of probiotic studies in IBS patients found significant relief of pain and
bloating with the use of Bifidobacterium Breve, B.
longum and Lactobacillus acidophilus species compared
to placebo.
However, there was no
change in stool frequency or consistency.
Note: Large-scale studies of well-phenotyped IBS
patients, Probiotics have
been only -20% effective as prophylaxis
Harrison’s principles of internal medicine, 19th Ed,
P-797, 857, 917, 1880, 1922
Traveler’s diarrhea
·
A meta-analysis
suggests that probiotics may lessen the likelihood of traveler’s diarrhea by -
15%.
C. difficile associated
diarrhea
·
Preliminary data
suggest a role for probiotics in the prevention of C. difficile associated diarrhea in patients in whom
systemic antibiotic therapy is being initiated.
Infectious diarrhea and
irritable bowel syndrome
·
Probiotics
containing active bacterial cultures are used as adjuncts in some cases of
infectious diarrhea and irritable bowel syndrome. Probiotics that selectively
nourish benign commensal bacteria may ultimately show benefit in functional
disorders as well.
Antibiotic-associated
diarrhea
·
Amoxicillin can
also lead to antibiotic-associated diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, skin
rash, and allergic reaction. Concomitant use of
probiotics may ameliorate some of the antibiotic side effects.
Kumar & Klark’s Clinical Medicine, 8th Ed,
P-280-81
- Probiotics are live microorganisms which
when ingested can modify the composition of enteric microflora.
- Commonly used probiotics are
lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, non-pathogenic E. coli.
Pouchitis
Kumar & Klark’s Clinical Medicine, 8th Ed, P-280-81
·
Pouchitis is
inflammation of the ileal pouch (an artificial rectum surgically created out of
ileal gut tissue in patients who have undergone a colectomy), which is created
in the management of patients with ulcerative colitis, indeterminate colitis,
familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), or, rarely, other colitides.
·
The probiotic has
been shown to be effective to prevent the onset of pouchitis and to maintain
remission in pouchitis patients with antibiotic induced mucosal healing.
·
Pouchitis– Probiotics
can prevent onset and maintain a remission.
CMDT, Current Medical Diagnosis & treatment 2015, P-644, 646
·
Probiotics
containing nonpathogenic strains of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, and
streptococci (VSL#3) are effective in the maintenance of remission in patients
with recurrent pouchitis.
Ulcerative colitis
Kumar & Klark’s Clinical Medicine, 8th Ed,
P-280-81
·
E. coli Nissle 1914 may be useful in maintaining
remissions in ulcerative colitis.
CMDT, Current Medical Diagnosis & treatment 2015, P-644, 646
·
Probiotics—VSL#3 (two
packets twice daily), a probiotic compound containing eight different
nonpathogenic strains of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, and streptococci, has
demonstrated significant benefit versus placebo in the treatment of mild to
moderate ulcerative colitis in two randomized, controlled multicenter trials.
Although its efficacy relative to
other agents is unclear, it may be considered as an adjunctive therapy for mild
to moderate disease.
Diverticular disease
Harrison’s principles of internal medicine, 19th Ed,
P-1972
·
Probiotics are
being increasingly used by gastroenterologists for multiple bowel disorders and
have been shown to prevent recurrence of diverticulitis. Specifically
probiotics containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium strains
have been shown to be beneficial.
CMDT, Current Medical Diagnosis & treatment 2015, P-632
·
C difficile is acquired in approximately 20% of
hospitalized patients, most of whom have received antibiotics that disrupt the
normal bowel flora and thus allow the bacterium to flourish.
·
C difficile colitis will develop in approximately
one-third of infected patients. In clinical trials, prophylactic administration
of the probiotics containing Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, and
Streptococcus thermophilus, to hospitalized patients who are
receiving antibiotics reduced the incidence of C difficile–associated
diarrhea.




Comments
You must login to write comment