Guidelines of Probiotics by World Gastroenterology Organization
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host.
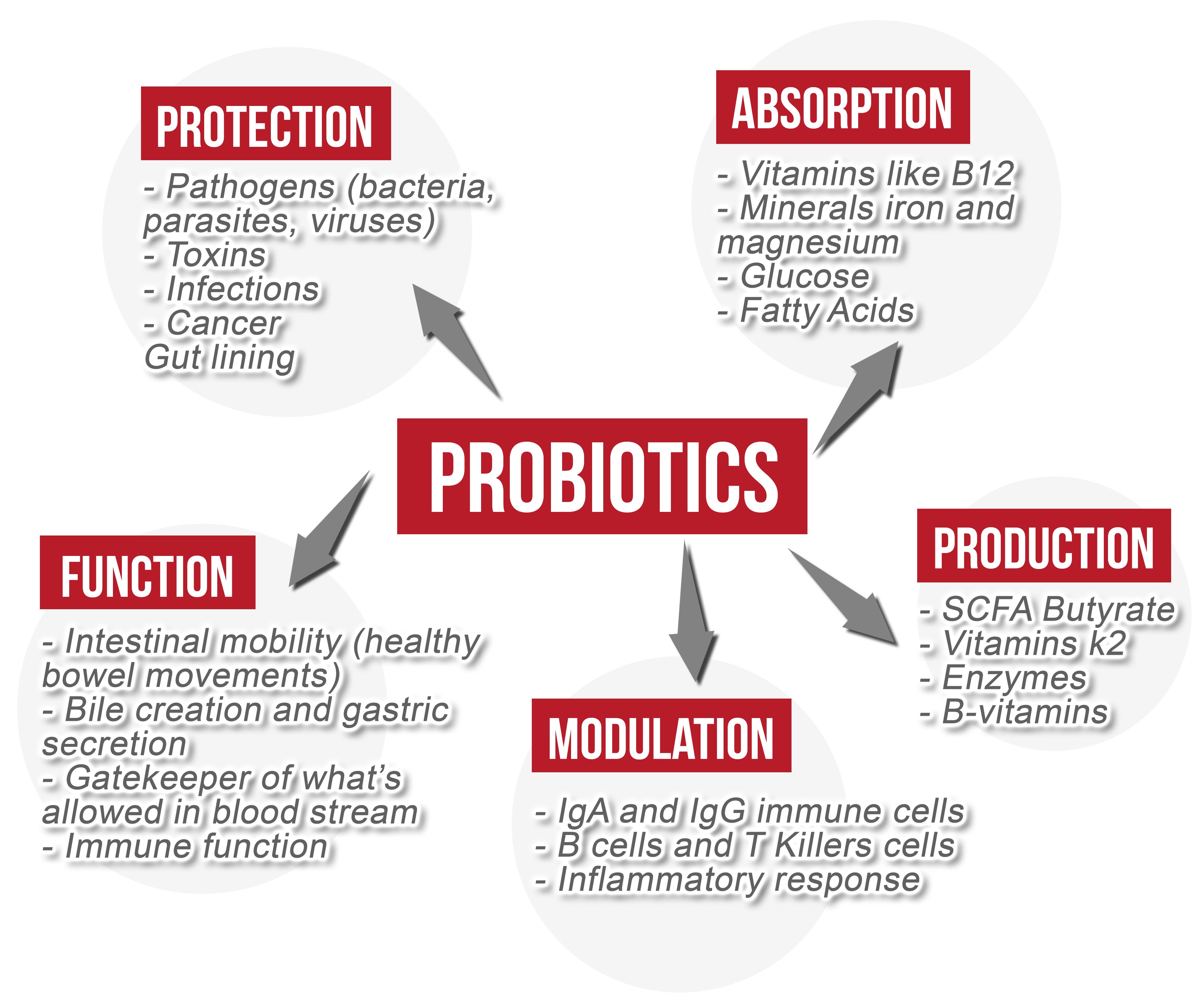
Current insights into the clinical applications for various probiotics in gastroenterology are summarized below:
Doctors Liked to Read More
Treatment of acute diarrhea
- Some probiotic strains are useful in reducing the
severity and duration of acute infectious diarrhea in children. Oral
administration shortens the duration of acute diarrheal illness in
children by approximately 1 day.
Note: However, the mechanisms of action may be
strain-specific.
Prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- In the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea,
there is strong evidence of efficacy in adults or children who are
receiving antibiotic therapy.
Prevention of Clostridium difficile diarrhea
- A 2016 meta-analysis concluded that probiotics can
reduce the risk of developing C. difficile–associated
diarrhea in patients receiving antibiotics.
Note: However, the authors caution that additional
studies are needed in order to determine the best dosage and strain.
- There is suggestive evidence that several probiotic
strains are useful in improving the immune response. Evidence suggestive
of enhanced immune responses has been obtained in studies aimed at
preventing acute infectious disease (nosocomial diarrhea in children,
influenza episodes in winter) and studies that tested antibody responses
to vaccines.
Pouchitis
- There is good evidence for the usefulness of certain probiotics in preventing an initial attack of pouchitis, and in preventing further relapse of pouchitis after the induction of remission with antibiotics. Probiotics can be recommended to patients with pouchitis of mild activity, or as maintenance therapy for those in remission.
Ulcerative colitis
- Certain probiotics have been found to be safe and as
effective as conventional therapy in achieving higher response and remission
rates in mild to moderately active ulcerative colitis in both adult and
pediatric populations.
- Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus
delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus improve lactose
digestion and reduce symptoms related to lactose intolerance. This was
confirmed in a number of controlled studies with individuals consuming yogurt
with live cultures.
- Probiotic supplementation reduces the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm neonates. Meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials have also shown a reduced risk of death in probiotic-treated groups, although not all probiotic preparations tested are effective.
·
https://www.worldgastroenterology.org/guidelines/global-guidelines/probiotics-and-prebiotics/probiotics-and-prebiotics-english
·
Lau CS, Chamberlain RS. Probiotics are effective at
preventing Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: a systematic review and
meta-analysis. Int J Gen Med. 2016 Feb 22;9:27–37.
·
Hamad A, Fragkos KC, Forbes A. A systematic review and
meta-analysis of probiotics for the management of radiation induced bowel
disease. Clin Nutr Edinb Scotl. 2013 Jun;32(3):353–60.
·
Dang Y, Reinhardt JD, Zhou X, Zhang G. The effect of
probiotics supplementation on Helicobacter pylori eradication rates and side
effects during eradication therapy: a meta-analysis. PloS One.
2014;9(11):e111030.
·
Grossi E, Buresta R, Abbiati R, Cerutti R, Pro-DIA
study group. Clinical trial on the efficacy of a new symbiotic formulation,
Flortec, in patients with acute diarrhea: a multicenter, randomized study in
primary care. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010 Sep;44 Suppl 1:S35–41.
·
Allen SJ, Martinez EG, Gregorio GV, Dans LF.
Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2010;(11):CD003048.
·
Höchter W, Hagenhoff G. (Saccharomyces boulardii in
acute adult diarrhea: efficacy and tolerability of treatment.). Munch Med
Wochenschr. 1990;(132):188–192.
·
Hempel S, Newberry SJ, Maher AR, Wang Z, Miles JNV,
Shanman R, et al. Probiotics for the prevention and treatment of
antibiotic-associated diarrhea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA.
2012 May 9;307(18):1959–69.
·
Szajewska H, Kołodziej M. Systematic review with
meta-analysis: Saccharomyces boulardii in the prevention of
antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015
Oct;42(7):793–801.
·
Cimperman L, Bayless G, Best K, Diligente A, Mordarski
B, Oster M, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study
of Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 for the prevention of antibiotic-associated
diarrhea in hospitalized adults. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 Oct;45(9):785–9.
·
Ouwehand AC, DongLian C, Weijian X, Stewart M, Ni J,
Stewart T, et al. Probiotics reduce symptoms of antibiotic use in a hospital
setting: a randomized dose response study. Vaccine. 2014 Jan 16;32(4):458–63.
Note: For informational
purposes only. Consult your textbook for advising your patients.




Comments
You must login to write comment