Escitalopram approved by the FDA for the treatment of Depression
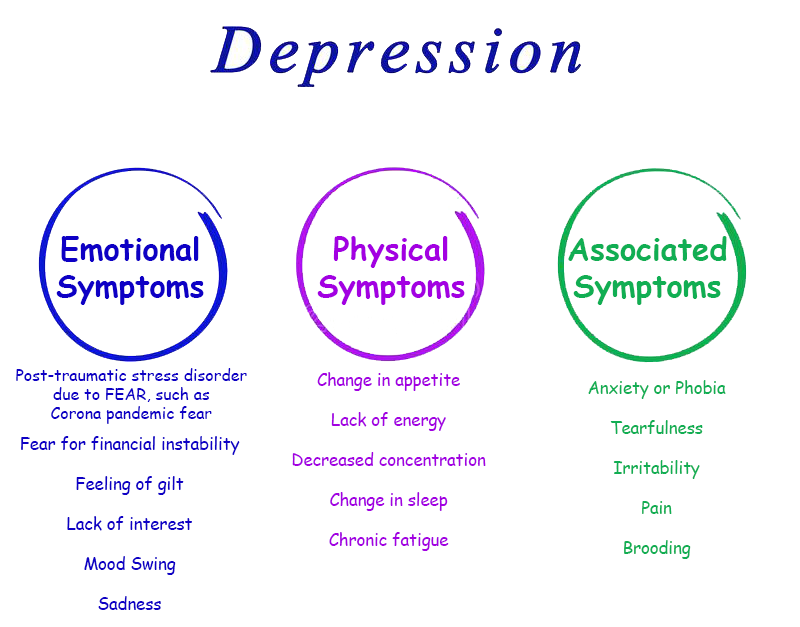
Depression is a mood disorder that involves a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest which interferes with daily functioning.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder. SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants as first-line agents for initial treatment of major depression in adults.
Doctors Liked to Read More
Numerous trials have demonstrated the efficacy of SSRIs in the
treatment of depression. In addition, SSRIs have been proved effective in
treating anxiety disorders, including obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD),
panic disorder, and social phobia.
Escitalopram is the newest and
most selective of the SSRIs approved by the FDA for the treatment of
depression.
Major Depressive Disorder,
Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
·
The recommended dosage of escitalopram is 10 mg
once daily. May increase to 20 mg/day after 1 week
·
No dosage adjustments are needed in patients
with hepatic impairment or mild to moderate renal impairment.
·
The potential for drug interactions is low.
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2010/0515/p1205.html
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2003/0201/p547.html
https://www.aafp.org/afp/2011/0515/p1219.html
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC315490/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3183928/
Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients with Major
Depressive Disorder. Third Edition. American Psychiatric Association. November
2010.
https://psychiatryonline.org/pb/assets/raw/sitewide/practice_guidelines/guidelines/mdd.pdf.
https://www.psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/clinical-practice-guidelines
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/conditions-and-diseases/mental-health-and-behavioural-conditions/depression
Note: For informational purposes only. Consult your
textbook for advising your patients.




Comments
You must login to write comment